KnowBe4 Says New CryptoWall 3.0 Ransomware Makes Paying Ransom "Easier"
'Ironically, as cyber criminals get more sophisticated, so do their efforts to improve their extortion methods.'
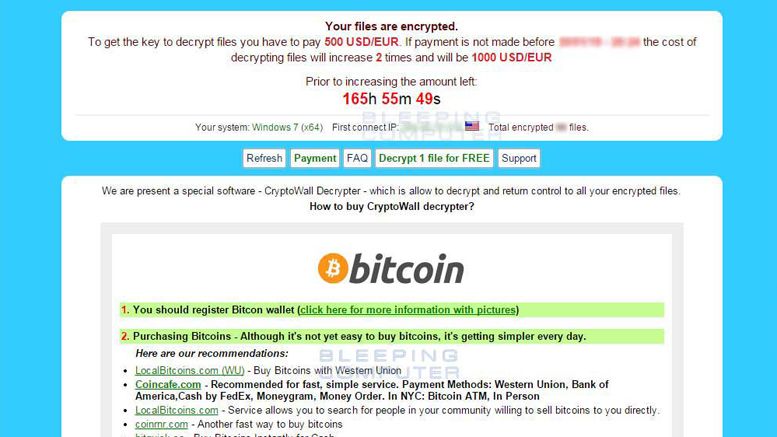
If there was any doubt that CryptoWall ransomware is a successful business model for cybercriminals, infecting over 700,000 victims thus far, the latest version will attempt to improve those numbers. A new version of CryptoWall dubbed 3.0 has been released a few days ago with new gateways that are used to access the CryptoWall decryption site. The deadlines for ransomware payment have also been extended from 5 days to a full week and the ransom note file names have been made easier to read with detailed information on how to access the ransom payment site. In the name of improved “customer service," these new features make it even easier to pay up when files have been hijacked.
According to KnowBe4 CEO Stu Sjouwerman, “Ironically, as cyber criminals get more sophisticated, so do their efforts to improve their extortion methods. While a hard working criminal is an oxymoron, CryptoWall 3.0 shows they are working diligently to make the ransom payment and decryption process easier.”
While phishing attacks are the most common way ransomware hits an organization, infections occur through multiple attack vectors, including email attachments, malicious PDF files and like those before it, this new version is also being distributed through drive-by-download attacks or other malware already installed on the personal computer.
In a new analysis published by Cisco, their team reports that the new variant of CryptoWall is able to distinguish between 32- and 64-bit architectures and to execute different versions for each.The software also checks if the system it is infecting is in a Virtual Machine environment with anti-AM and anti-emulation checks to hamper identification via sandboxes. If it detects this is the case, it does not execute in that environment, making the malware analysis either impossible or much harder.
The additional gateways allow an infected user to access the CryptoWall decryption site without having to install the TOR browser software, a difficult task for a non-techie. It does this by routing the user to another anonymous network called I2P.
Sjouwerman stated, “IT managers should back up their servers and frequently test the backups to ensure they work, as backup failure rates can go as high as 60% at times. If you are using cloud backup, make sure you use versioning, as ransomware can attack other drives and cloud storage. Without a working backup, your options are really pay the ransom or lose your data. Even with a backup, it may be cheaper to pay the ransom. One of the most cost effective ways to avoid ransomware is to step your users through the Kevin Mitnick Security Awareness Training and follow up with frequent anti-phishing testing to keep security top of mind. We are so confident it works. If you’ve trained your users, send them simulated phishing attacks every month, and if you still get hit, we’ll pay your Bitcoin ransom.”
About Stu Sjouwerman and KnowBe4
Stu Sjouwerman (pronounced “shower-man”) is the founder and CEO of KnowBe4, LLC, which provides web-based Security Awareness Training (employee security education and behavior management) to small and medium-sized enterprises. A data security expert with more than 30 years in the IT industry, Sjouwerman was the co-founder of Inc. 500 company Sunbelt Software, an award-winning anti-malware software company that he and his partner sold to GFI Software in 2010. Realizing that the human element of security was being seriously neglected, Sjouwerman decided to help entrepreneurs tackle cybercrime tactics through advanced security awareness training. KnowBe4 services hundreds of customers in a variety of industries, including highly-regulated fields such as healthcare, finance and insurance and is experiencing explosive growth with a surge of 427% in 2013 alone. Sjouwerman is the author of four books, with his latest being Cyberheist: The Biggest Financial Threat Facing American Businesses.
About Kevin Mitnick
Kevin Mitnick is an internationally recognized computer security expert with extensive experience in exposing the vulnerabilities of complex operating systems and telecommunications devices. He gained notoriety as a highly skilled hacker who penetrated some of the most resilient computer systems ever developed. Today, Mitnick is renowned as an information security consultant and speaker, and has authored three books, including The New York Times best seller Ghost in the Wires. His latest endeavor is a collaboration with KnowBe4, LLC.
Related News





